If you run a website long enough, you almost never end up with just one domain. You buy a few variations to protect your brand. Maybe you change your business name. Maybe you grab a shorter URL for ads or social media. Suddenly, you’ve got several domains and one big question: where should they all point?
Domain forwarding solves that problem. It quietly sends visitors from one domain to another, so no one lands on the wrong page or a dead link. It keeps your brand consistent, avoids SEO headaches, and ensures people get where they expect to go.
In this guide, we’ll walk through how domain forwarding actually works, the different redirect options available, and what to watch out for if you want to keep your search rankings safe.
What is Domain Forwarding?
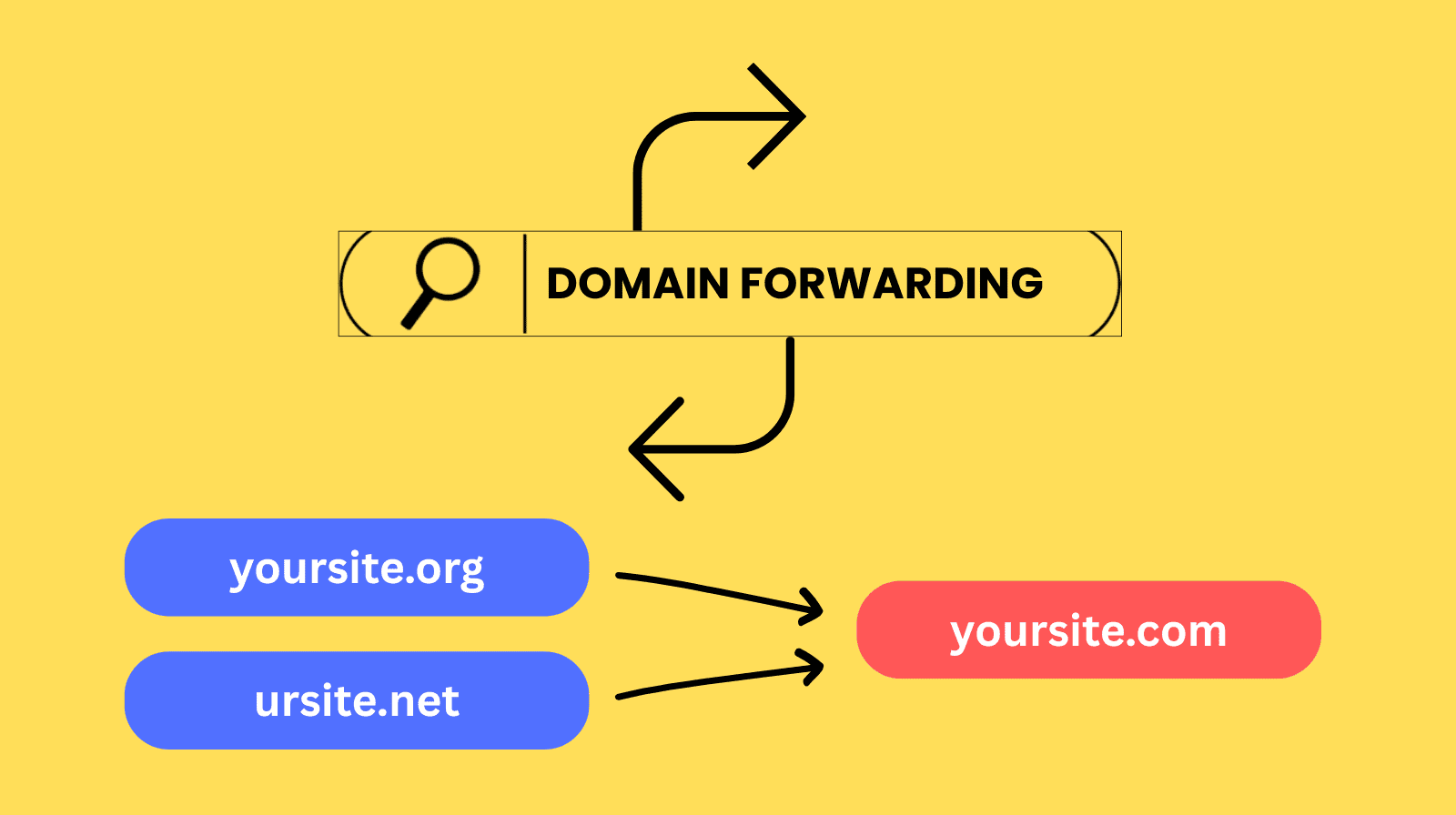
Domain forwarding, also known as URL redirection or web forwarding, is a service that automatically directs visitors from one domain name to another. When someone types a forwarded domain into their browser, the server sends a command to the browser to load a different destination URL instead.
You can use domain forwarding to point a domain to:
- Another primary website (e.g., redirecting yourbrand.net to yourbrand.com).
- A specific page or “microsite” within a larger website.
- A social media profile, such as a Facebook page or LinkedIn company profile.
Basically, it acts as a permanent or temporary “Change of Address” notice for the internet, ensuring that your traffic isn’t lost if a user enters an old or alternative web address.
Domain Forwarding vs. URL Forwarding
While it’s common to use these terms interchangeably, there is a slight technical difference:
- Domain Forwarding: Usually refers to redirecting an entire domain (and all its traffic) to a new home.
- URL Forwarding: Often refers to redirecting a specific, individual page path (e.g., mysite.com/old-page to mysite.com/new-page).
Why Use Domain Forwarding?
Domain forwarding is a practical tool for growing a brand and managing an online presence. It helps you capture more traffic and protect your business identity. Here are the most common reasons to use it:
- Brand Protection: Many business owners buy common variations of their domain name. For example, if you own the .com version, you might also buy the .net, .org, or .biz versions. Forwarding these to your main site prevents competitors from using them and ensures your customers find you.
- Handling Typos: If your brand name is hard to spell, you can buy the misspelled version of the domain and forward it to the correct one. This captures visitors who make a mistake when typing your address.
- Rebranding: If you change your company name, you don’t want to lose the traffic going to your old domain. Forwarding the old address to the new one keeps your existing audience connected to your business.
- Marketing Campaigns: You can use short, catchy domains for ads. Instead of asking customers to remember a long link like website.com/products/seasonal-sale-2026, you can forward a simple domain like getsale.com directly to that page.
- Social Media Links: If you don’t have a full website yet, you can forward your domain name directly to your Instagram, Facebook, or LinkedIn profile. This makes your brand look more professional on business cards or in ads.
Types of Domain Forwarding
Choosing the right redirect type is the most important part of domain forwarding. Each type sends a different signal to search engines about how to treat your website traffic and authority.
301 Redirect (Permanent)
A 301 redirect is a permanent move. It tells search engines and browsers that the old web address is gone for good and has a new home. This is the best choice for SEO because it transfers the ranking power and credibility from your old domain to your new one.
If you are rebranding or moving your site to a new name, this is the option you should choose to keep your search engine positions intact.
302 Redirect (Temporary)
A 302 redirect is a temporary move. It informs search engines that the content has moved to a new address for a short period, but will eventually return to the original URL.
Because it is temporary, it does not transfer any SEO value or link equity to the new address. You should use this when you are doing website maintenance or running a seasonal promotion that will only last a few weeks.
Wildcard Forwarding
Wildcard forwarding is a specific setting that helps you manage subdomains. Instead of setting up a separate rule for every part of your site, a wildcard redirect sends every variation of your domain to the same destination.
For example, if someone types “https://www.google.com/search?q=store.yourdomain.com” or “https://www.google.com/search?q=help.yourdomain.com,” they will all be forwarded to the primary site you have chosen. This ensures that no matter what prefix a visitor adds to your domain, they never hit a dead end.
Masked Forwarding
Masked forwarding (sometimes called cloaking) keeps the original domain name in the browser address bar while showing the content of the new site. While this might seem cleaner, it causes major problems. Search engines may penalize your site for duplicate content, and many modern security settings will block masked sites entirely.
Most professionals recommend avoiding this method and using a standard 301 redirect instead.
Domain Forwarding and SEO: Best Practices
Domain forwarding directly affects how search engines like Google view your website. If you set it up correctly, you can move your site without losing your rankings. If you do it poorly, you may lose years of search visibility. Following these best practices will help you keep your SEO strong.
Focus on Link Equity
When you use a 301 redirect, search engines pass the “ranking power” of your old domain to the new one. This includes the value of all the backlinks you have earned over time.
To get the most benefit, you should keep the old domain active for as long as possible so that the redirect continues to signal to search engines that your site has moved.
Map Pages Accurately
One common mistake is redirecting every page of an old website to the homepage of a new website. This is often called a “lazy redirect.” It is much better for SEO to map old pages to their specific new counterparts.
For example, if you have an old “About Us” page, it should forward to the new “About Us” page. This keeps the content relevant for the user and helps search engines understand that the specific topic of that page still exists.
Maintain SSL Certificates
Security is a major ranking factor. If your old domain used HTTPS, you must ensure that the SSL certificate remains active even after you start forwarding. If a user clicks an old link and receives a “Your connection is not private” warning, they will likely leave immediately. Most browsers will block the redirect entirely if the security certificate is missing or expired.
Avoid Redirect Chains
A redirect chain happens when you forward Domain A to Domain B, which then forwards to Domain C. These chains slow down your website because the browser has to make multiple requests before it can show any content. This slow speed can hurt your SEO.
Always try to forward a domain directly to its final destination in a single step.
Check for Duplicate Content
If you have multiple domains pointing to the same site without proper forwarding, search engines might see them as separate websites with identical content. Now this can lead to a penalty.
Proper domain forwarding tells search engines that all these addresses are actually just different paths to one single, authoritative source.
How to Set Up Domain Forwarding
Setting up domain forwarding is straightforward, but the steps may vary slightly depending on the company you use to manage your domain. While the interface for a registrar like GoDaddy might look different from that of Namecheap or Google, the underlying technical logic remains the same.
Below is a detailed guide to completing the setup.
Step 1: Access Your Domain Management Settings
First, log in to the account you used to purchase your domain. Look for a section labeled “My Domains,” “Domain Manager,” or “DNS Management.” Once you find the list of your domains, click the domain you want to forward.
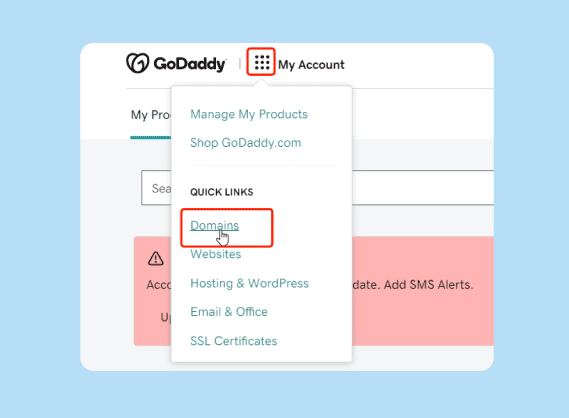
GoDaddy My Account dashboard showing the list of owned domains
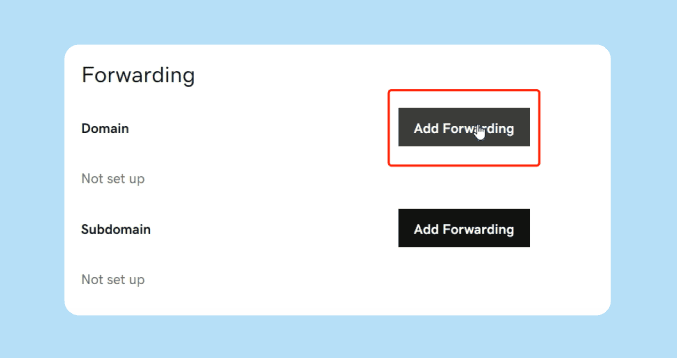
Step 2: Locate the Forwarding or Redirect Option
Most registrars have a dedicated “Forwarding” or “Redirect” section. If you do not see this immediately, look under “Advanced Settings” or “DNS Records.” There is usually a button or link that says “Add Forwarding” or “Set Up Redirection.”
Step 3: Enter the Destination URL
In the forwarding settings, you will see a field to enter the “Forward To” or “Destination” address. It is very important to include the full web address, starting with http:// or https://. If your destination site uses a security certificate, always use https:// to ensure a secure connection for your visitors.
Step 4: Choose Your Redirect Type
You will be asked to select between a 301 (Permanent) or 302 (Temporary) redirect. As discussed earlier, use the 301 option if you want to transfer your SEO value and you have no plans to use the old address again. Choose 302 only if you are doing a short-term test or maintenance.
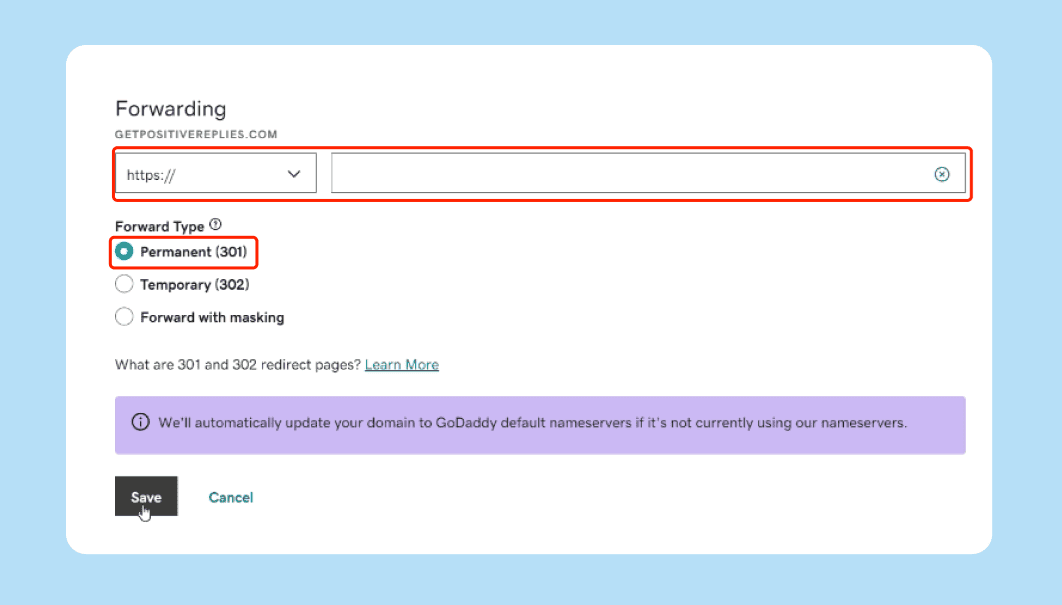
Step 5: Select Forwarding with or without Masking
Your registrar may ask if you want to use “Forward Only” or “Forward with Masking.” Always select “Forward Only” unless you have a very specific technical reason to do otherwise. Masking can cause your site to break on mobile devices and prevent search engines from properly indexing your content.
Step 6: Configure Path Forwarding (Optional)
Some services offer “Path Forwarding.” This means if someone types oldsite.com/contact, they will be automatically sent to newsite.com/contact. If you do not enable this, every visitor will be sent to the main homepage of the new site, regardless of which page they were trying to reach.
If you are moving an entire website, enabling path forwarding is much better for the user experience.
Step 7: Save and Wait for Propagation
Once you save your changes, the update will not happen instantly. It takes time for the new instructions to spread across the internet. This process is called DNS propagation. It usually takes anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours, but in some cases, it can take up to 48 hours to work globally.
Domain Forwarding Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
Even though domain forwarding is simple to set up, small mistakes can lead to broken links or lost traffic. If your redirect is not working as expected, it is likely due to one of the common issues listed below:
The Redirect Loop
A redirect loop occurs when Domain A is configured to forward to Domain B, but Domain B is also configured to forward back to Domain A. This creates a circular redirect loop that the browser cannot break out of. Eventually, it results in an error message that says “Too many redirects.”
Always double-check your settings to ensure the destination URL is not pointing back to the source.
The Email Forwarding Trap
Many people forget that domain forwarding only handles web traffic. If you forward yourdomain.net to [suspicious link removed], any emails sent to info@yourdomain.net will not automatically move.
If you want to keep receiving those emails, you must set up a separate email forwarding rule through your domain registrar or email provider. Failing to do this can lead to missed messages from clients and partners.
SSL Certificate Errors
If your destination site uses https, but your old domain does not have a valid SSL certificate, many browsers will show a security warning to the user before the redirect happens. This scares away visitors. For the smoothest transition, make sure both the old domain and the new destination have active SSL certificates.
Wait for DNS Propagation
When you change domain settings, things don’t update right away. Even if everything is set up correctly, it can take time for the new details to reach servers around the world. This delay is called DNS propagation, and it’s completely normal.
Most of the time, the update goes through within minutes. Occasionally, though, it can drag on for a day or two. If your redirect doesn’t work straight away, give it a few hours, clear your browser cache, and then check again.
Forgotten Subdomains
Another common mistake in domain forwarding is forwarding the main domain but forgetting about the “www” version. For example, [suspicious link removed] might forward correctly, but [suspicious link removed] might still show an error page.
When setting up your redirect, confirm you have applied the rule to both versions or used a wildcard setting to cover all possibilities.
Conclusion
Domain forwarding is an important tool for anyone managing a brand online. It helps you keep your traffic organized, protects your business name, and makes sure your customers never land on a broken page.
Whether you are moving to a new name or just connecting a few extra domains to your main site, the process is simple once you know which redirect type to use.
The most important step is to choose a 301 redirect for permanent changes so you do not lose your search engine rankings. Always test your links after setting them up, and remember to handle your email settings separately.
With these steps in place, you can grow your online presence with confidence and keep your audience connected to your brand.
Domain Forwarding FAQs
What is domain forwarding?
Domain forwarding is a service that automatically sends visitors from one web address to another. It allows you to point multiple domains you own to a single website or social media page.
What is the difference between redirect and forwarding a domain?
In most cases, they are the same thing. Domain forwarding is the specific service provided by domain registrars to point an entire domain, while a redirect is the technical process used to move traffic from one URL to another.
Does domain forwarding affect SEO?
Yes, but it is usually better to use a 301 redirect. This type of forwarding tells search engines the move is permanent and transfers the ranking power and authority from the old domain to the new one.
How to set up domain forwarding?
Log in to your domain registrar, find the DNS or Domain Management settings, and look for the “Forwarding” option. Enter your destination URL, select the redirect type (301 or 302), and save your changes.
 DomCop
DomCop