Imagine you’ve found the perfect domain. It’s short, catchy, and has a great history. You buy it, full of plans, only to discover it’s been hit by a Google penalty.
A Google penalty is essentially a digital fine. It’s a punishment for websites that use “black-hat” or spammy tactics to cheat search results. If your domain is penalized, your rankings will drop dramatically, or your site might disappear from Google entirely.
In this guide, we will break down the two main types of Google penalties, show you the specific toxic issues to watch out for, and teach you how a proper Google penalties checker approach can protect your budget and your business.
Understanding the Two Types of Google Penalties
Does Google penalize websites? The short answer is yes, absolutely. Google uses these punishments to ensure that search results are high-quality and helpful to users, weeding out sites that try to manipulate the system.
These penalties fall into two main categories: Manual and Algorithmic.
Manual Penalties
Manual penalties are imposed when a human reviewer at Google determines that a page or site is directly violating Google’s spam policies.
- How it happens: A member of Google’s dedicated team manually reviews your site, often triggered by a user report or competitor flagging your site.
- How you find out: If your site is penalized manually, Google will send you a clear notification in the Manual Actions tab within Google Search Console. This message tells you exactly why your site was penalized (e.g., “Unnatural links to your site”).
You must fix the issue, document the steps you took, and then submit a Reconsideration Request to Google for review.
Algorithmic Penalties
Algorithmic penalties are applied automatically by Google’s vast search algorithms without human intervention. These penalties occur when your website fails to comply with a major algorithmic update.
- How it happens: These usually occur after a major update, such as Panda (focused on thin/low-quality content), Penguin (focused on spammy links), or the recent Helpful Content Update.
- How you find out: You usually do not get a direct notification. You discover it when your website experiences a sudden, severe drop in search traffic that corresponds exactly to the date of a known Google algorithm update.
You must identify the specific issue (e.g., low-quality content, slow speed) and fix it. Once Google’s automated bots crawl and re-assess the clean pages, your rankings should begin to recover.
The 4 Most Dangerous Penalties for Expired Domains
When you buy an expired domain, you are not just buying a name; you are buying the previous owner’s entire history, including their black-hat mistakes. These four issues are the most critical risks that domain buyers might inherit:
1. Unnatural/Low-Quality Inbound Links (The Penguin Risk)
This is one of the most common and difficult issues to fix. If the previous owner tried to cheat the system by buying links from spammy websites, link farms, or irrelevant foreign sites, your domain carries this toxic debt.
- What’s the Risk: Google’s Penguin algorithm is specifically designed to demote sites with this issue. If you inherit thousands of bad links, Google views your entire domain as untrustworthy.
- Fix: You must first use a backlink analysis tool to identify all the toxic links. Then, you should try to contact the linking site’s owner to request removal. For links you can’t remove, you must use the Google Disavow Tool to tell Google to ignore them.
Ahrefs Free Backlink Checker Tool
2. Thin Content / Low Quality Content
Google’s core mission is to deliver high-quality, relevant content that provides value. The Panda algorithm and the recent Helpful Content Update specifically target sites that fail this standard.
- What’s the Risk: If the previous site was full of automatically generated text, very short blog posts lacking depth, or duplicate content, your domain will struggle to rank. This is known as thin content.
- Fix: You need a full content audit. Delete or ‘noindex’ pages that are beyond saving. For pages you keep, you must significantly expand and improve them, ensuring they offer true E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust) to the reader.
3. Hacked Content or Website
Hackers often target established domains to insert malicious code, create hidden spam pages, or set up sneaky redirects without the owner even knowing.
- What’s the Risk: Google quickly detects hacked sites because they pose a security risk to users. Your entire site can be penalized and flagged with a “This site may be hacked” warning in search results.
- Fix: Immediately scan and clean the site to remove all malicious code. Once clean, strengthen security (update CMS, use two-step verification), and then check the Security Issues tab in Search Console for further guidance.
Security issues tab in Google Search Console
4. Cloaking and Sneaky Redirects
These are severe black-hat tactics that violate Google’s rules and result in a harsh manual penalty.
- What’s the Risk: Cloaking is showing a search engine one version of a page (often keyword-stuffed) and showing the human user a completely different page. Sneaky redirects send users to a totally irrelevant destination. Google views this as deliberate deception.
- Fix: You must immediately resolve all instances of variation between what Google’s bots see and what a user sees. Once fixed, you must submit a Reconsideration Request via the Manual Actions report.
Reconsideration request in Google Search Console
Essential Due Diligence: Using a Google Penalties Checker
When buying an expired domain, you must act like a security inspector. A Google penalties checker is not a single tool, but a methodical approach to analyzing the domain’s history to uncover inherited issues.
1. The Manual Actions Check (If Possible)
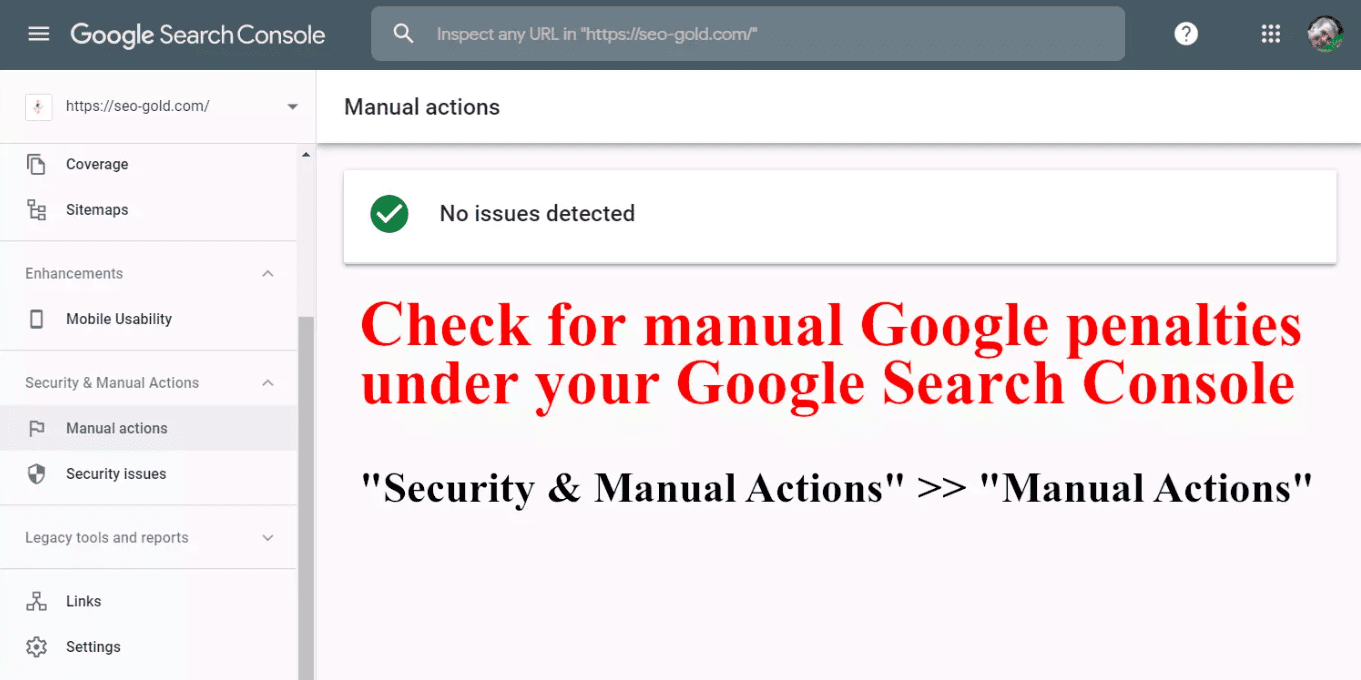
Check manual Google penalties under your Google Search Console
The first and easiest check is looking for a direct penalty flag. If you have temporary access to the domain’s Google Search Console (GSC) account, check the Manual Actions tab.
A direct report here confirms a human-issued penalty and specifies the exact problem you need to fix immediately. This is often only possible after the purchase has been made, but it is the definitive proof of a manual penalty.
2. The Traffic/Update Cross-Reference
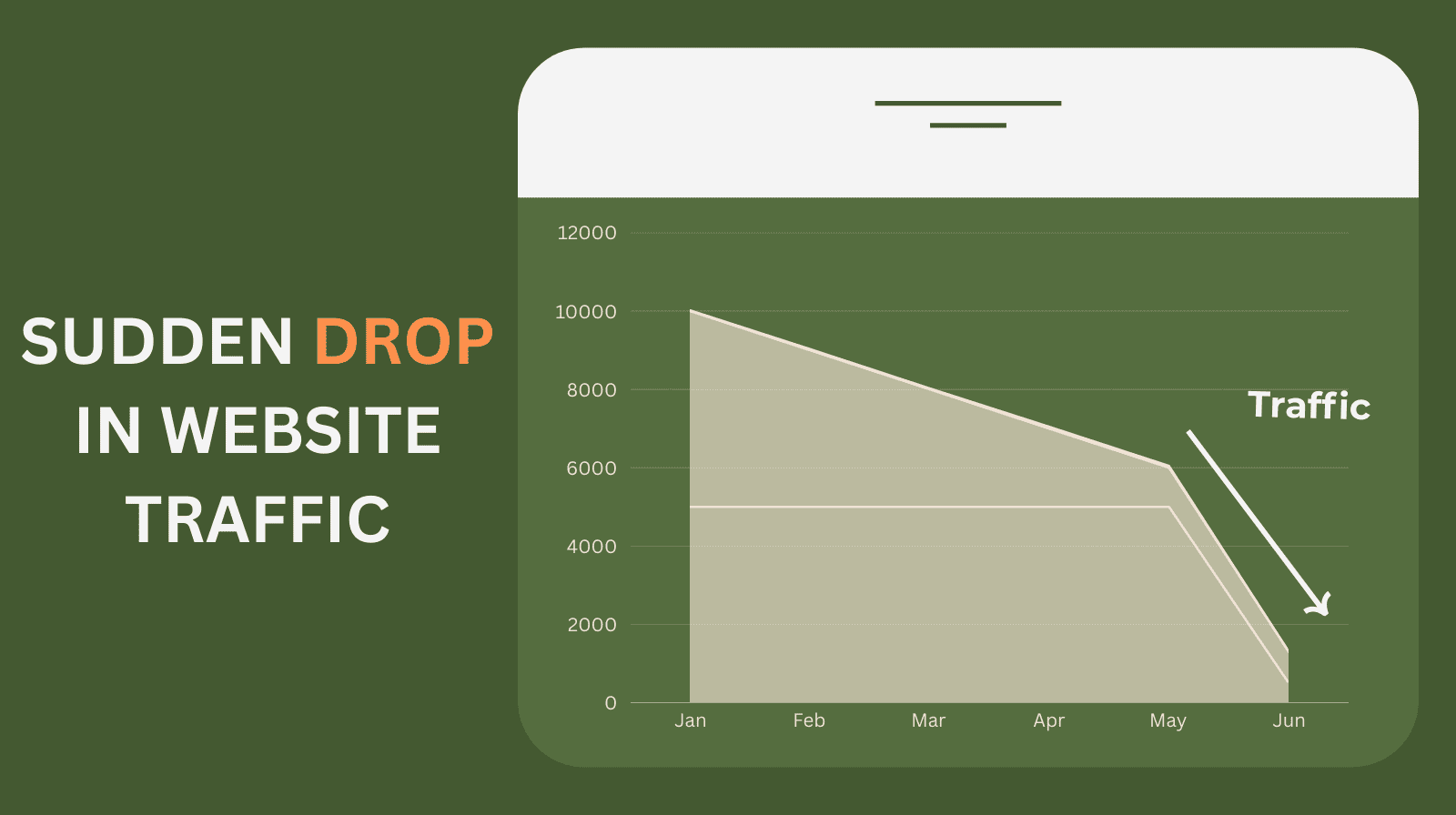
This method helps detect hidden algorithmic penalties, which is especially useful when GSC access is unavailable before purchase. You should use third-party tools to check the domain’s past organic traffic history.
Look for dramatic or sudden drops in traffic. Then cross-reference the dates of these drops with known dates of major Google algorithm updates, such as Panda or Penguin.
If a massive traffic drop lines up perfectly with a known penalty-related update, the domain likely carries a corresponding algorithmic penalty for low quality or spam.
3. Backlink Audit: Finding the Toxic Debt
Unnatural or toxic links are the most common inherited problem associated with the Penguin algorithm. You must use professional backlink analysis tools to review the domain’s incoming links.
You’re watching for a high number of links from questionable places, like irrelevant or foreign-language sites, obvious link directories, or domains with very low authority or high spam scores. If you find a lot of these, it’s a serious red flag.
4. History Snapshot Check
Check domain history to reveal all past visual issues
This check is very useful for revealing past visual issues like spam, cloaking, or severe niche changes. Use a service like Archive.org (Wayback Machine). Enter the domain and look at snapshots from different points in time.
Did the site suddenly switch to a foreign language? Was it full of spammy articles or advertisements? This visual inspection can uncover evidence of hacking, cloaking, or poor content quality left by a previous owner.
How To Get Rid of Google Penalties?
The recovery strategy is dictated by whether the penalty is manual or algorithmic.
Recovery from Manual Penalties
Manual penalties require direct communication with Google and a formal review process.
Implement Comprehensive Fixes
You must first completely resolve the exact issue cited in the Manual Actions tab of Google Search Console. For instance, if the penalty is for unnatural links to your site, you must contact webmasters to remove the links, and use the Google Disavow Tool for the links you cannot get removed.
If the penalty is for cloaking, you must ensure that the content presented to human users is identical to the content seen by Google’s crawlers.
Submit a Reconsideration Request
After cleaning up the site, you must submit a formal Reconsideration Request through GSC. This request acts as your documentation, explaining to the human reviewer the precise steps you took to make the site fully compliant with Google’s quality guidelines.
Recovery is only granted when a Google team member manually approves this request.
Recovery from Algorithmic Penalties
Algorithmic demotions stemming from updates like Panda (low-quality) or Penguin (spam links) require a site-wide cleanup rather than a single request.
The Content Audit (Panda/Helpful Content)
If the problem is thin content, you must perform a massive audit. This involves identifying low-value pages, deleting those that can’t be saved, and significantly improving others to meet high-quality, E-E-A-T standards. You must prove to the algorithm that you value the user experience.
The Link Cleanup (Penguin)
If the problem is a historic, site-wide issue with bad inbound links, even if you did not receive a manual action, you must still identify and use the Google Disavow Tool.
This proactively tells the Penguin algorithm to ignore those toxic links and is essential for clearing the inherited link debt of an expired domain.
General Compliance
For penalties related to mobile-friendliness or slow speed, you must update your code and servers. The domain will begin to recover only after Google’s crawlers find and index the fully compliant, improved pages.
How Long Does a Google Penalty Last?
There is no set time limit for a penalty; it lasts as long as the violation remains unfixed.
Manual Penalty Duration
This lasts until Google’s human reviewer manually approves your Reconsideration Request. It can take anywhere from a few days to weeks, depending on the severity and complexity of the violation.
Algorithmic Penalty Duration
This lasts until you fully address the violations on your site. Because this relies on Google’s automated crawlers finding your new, clean pages, the duration depends on the size of your site and how often Google crawls it.
Recovery can be quick if the fixes are easy, or it may take several months for full recovery if the issue is deep-seated (like thin content across thousands of pages).
Conclusion
The risk of inheriting a Google penalty is one of the biggest concerns when buying expired domains. Penalties don’t come with any direct fee, but they can cost you heavily through lost traffic and months of cleanup work.
To protect your investment, follow a full Google-penalty check: audit backlinks, look for major historical traffic drops, and review the site’s past through Archive.org.
Remember, a penalty sticks until you correct the issues and Google reevaluates the site. If the domain’s history looks suspicious, it’s usually smarter to walk away.
 DomCop
DomCop